In today’s fast-paced world, technology is advancing at an unprecedented rate. From artificial intelligence to quantum computing, tech innovations are changing the way we live, work, and interact. This article will explore the top 10 cutting-edge tech innovations that are making waves in various industries. We’ll delve into their challenges, future outlook, and global impact.
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI)

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been a game-changer in numerous fields, including healthcare, finance, and customer service. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make predictions with remarkable accuracy.
Technological Advancements
AI technology has evolved rapidly, with advancements in machine learning, deep learning, and neural networks. These technologies enable AI systems to learn from data, improve over time, and make autonomous decisions. The development of natural language processing (NLP) allows AI to understand and generate human language, enhancing communication between humans and machines.
Real-World Applications
AI is being implemented in various real-world applications, such as predictive analytics, personalized medicine, and automated customer support. In healthcare, AI assists in diagnosing diseases, predicting patient outcomes, and personalizing treatment plans. In finance, AI algorithms detect fraudulent activities, assess credit risks, and optimize trading strategies.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite its potential, AI faces challenges such as ethical concerns, data privacy, and the need for substantial computational power. Ensuring AI systems are transparent, fair, and unbiased is crucial to their acceptance and success. Nevertheless, the future outlook for AI is promising, with continuous advancements expected to enhance its capabilities and broaden its applications.

Global Impact
AI’s global impact is profound, from improving medical diagnoses to enabling autonomous vehicles. AI-driven innovations are poised to revolutionize various sectors, leading to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced user experiences. Companies investing in AI research and development are poised to lead the market in the coming years, driving economic growth and technological progress.
2. Quantum Computing
Quantum computing promises to revolutionize computing by performing complex calculations at unprecedented speeds. Unlike classical computers, which use bits, quantum computers use qubits, allowing them to process multiple possibilities simultaneously.
Technological Foundations
Quantum computing is based on principles of quantum mechanics, such as superposition and entanglement. Superposition allows qubits to exist in multiple states simultaneously, while entanglement enables qubits to be interconnected, sharing information instantly. These properties provide quantum computers with immense computational power and speed.
Innovation and R&D
Research and development in quantum computing are accelerating, with tech giants like IBM and Google making significant strides. IBM’s Quantum Experience and Google’s Quantum Supremacy are notable milestones in the field. However, practical, large-scale quantum computers are still in the experimental stage, requiring advancements in hardware, error correction, and quantum algorithms.

Potential Applications
Quantum computing’s potential applications include cryptography, material science, and drug discovery. In cryptography, quantum computers can break current encryption methods, necessitating the development of quantum-resistant algorithms. In material science, quantum simulations can lead to the discovery of new materials with unique properties. In drug discovery, quantum computing can accelerate the identification of potential drug candidates and optimize molecular structures.
Market Dominance and Global Impact
Quantum computing promises to disrupt various industries and create new market leaders. Companies investing in quantum research and development are likely to gain a competitive edge, driving innovation and economic growth. The global impact of quantum computing extends to national security, healthcare, and technology, shaping the future of various sectors.

3. 5G Technology

5G technology is the next generation of wireless communication, offering faster speeds, lower latency, and greater connectivity. It is expected to enable innovations like smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
Technological Enhancements
5G technology provides significant enhancements over previous generations, including increased bandwidth, higher frequency bands, and advanced antenna technologies. These improvements allow for faster data transmission, reduced latency, and more reliable connections, supporting a wide range of applications and services.
Real-World Implementations
The rollout of 5G is enabling real-world implementations such as smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and enhanced mobile experiences. In smart cities, 5G supports IoT devices for efficient energy management, traffic control, and public safety. Autonomous vehicles rely on 5G for real-time communication with infrastructure and other vehicles, ensuring safety and efficiency.
Challenges and Future Outlook
The rollout of 5G faces challenges such as infrastructure costs, regulatory hurdles, and cybersecurity concerns. Building the necessary infrastructure, including base stations and fiber-optic networks, is costly and time-consuming. Regulatory approval and spectrum allocation are also critical for widespread adoption. However, the future outlook for 5G is bright, with widespread adoption anticipated in the coming years.

Value Addition
5G technology will add immense value by enhancing communication, enabling real-time data exchange, and supporting the growth of IoT ecosystems. Improved connectivity will drive innovation in various sectors, from healthcare and education to entertainment and manufacturing. The economic impact of 5G is expected to be substantial, creating new business opportunities and transforming industries.
4. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology provides a decentralized, secure way to record transactions. It is best known for powering cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, but its potential applications extend far beyond digital currencies.
Technological Foundations
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that ensures transparency, security, and immutability of data. Each block in the chain contains a list of transactions, and once added, it cannot be altered or deleted. This decentralized approach eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
Company Profiles
Numerous companies are exploring blockchain solutions, including IBM, Microsoft, and Ripple. IBM’s Hyperledger Fabric and Microsoft’s Azure Blockchain are leading platforms for enterprise blockchain applications. Ripple focuses on cross-border payments, providing faster and cheaper transactions compared to traditional methods.
Real-World Applications
Blockchain’s potential applications extend to various industries, including finance, supply chain management, and healthcare. In finance, blockchain enables secure and transparent transactions, reducing fraud and increasing trust. In supply chain management, blockchain ensures traceability and authenticity of products, improving efficiency and reducing counterfeiting. In healthcare, blockchain secures patient data and enhances data sharing among healthcare providers.
Market Dominance and Global Impact
Blockchain’s ability to provide transparency and security has the potential to revolutionize industries, disrupt traditional business models, and create new market leaders. Companies that adopt blockchain technology are likely to gain a competitive advantage, driving innovation and economic growth. The global impact of blockchain extends to financial inclusion, data privacy, and digital identity, shaping the future of various sectors.

5. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)

AR and VR technologies are transforming the way we experience the world. AR overlays digital information onto the physical world, while VR immerses users in a completely virtual environment.
Technological Advancements
AR and VR technologies have seen significant advancements in hardware, software, and content creation. Improved sensors, displays, and processors enhance the realism and responsiveness of AR and VR experiences. Software development kits (SDKs) and platforms like ARKit and Unity enable developers to create immersive and interactive applications.
Real-World Applications
AR and VR are being implemented in various real-world applications, such as gaming, education, healthcare, and retail. In gaming, VR provides immersive experiences, transporting players to virtual worlds. In education, AR enhances learning by overlaying interactive content onto textbooks and classrooms. In healthcare, VR is used for medical training, therapy, and pain management. In retail, AR allows customers to visualize products in their environment before making a purchase.
Innovation and R&D
Companies like Oculus (owned by Facebook) and Magic Leap are at the forefront of AR and VR innovation. Research and development efforts focus on improving hardware, software, and user experiences. Oculus has developed the Oculus Rift and Oculus Quest, providing high-quality VR experiences. Magic Leap’s AR headset offers advanced spatial computing capabilities, enabling new forms of interaction and creativity.
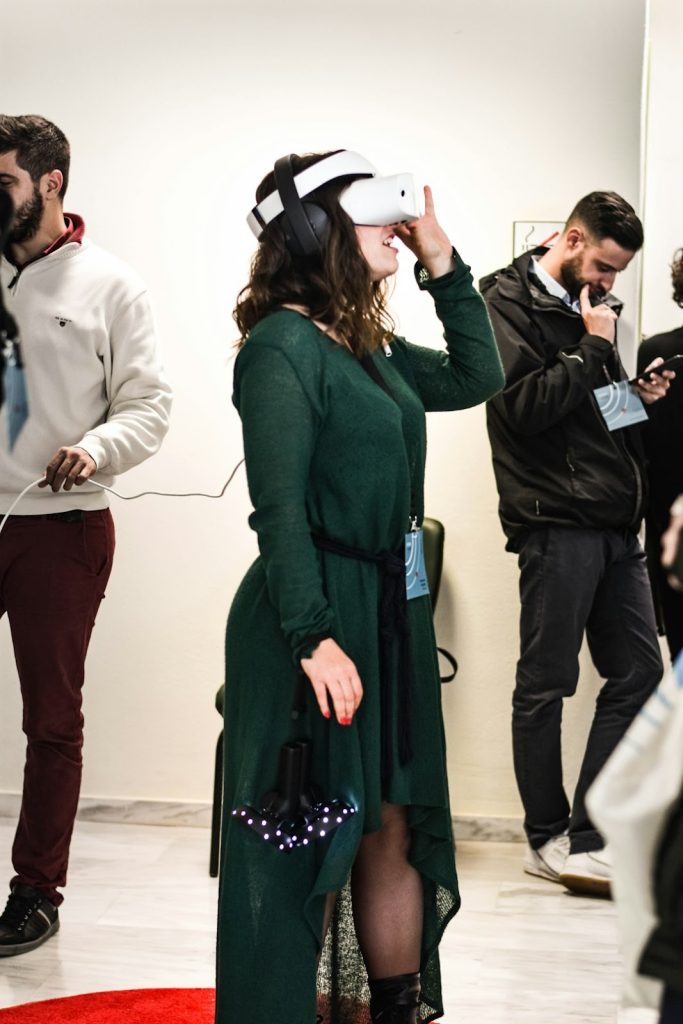

Future Outlook
The future outlook for AR and VR is promising, with applications in gaming, education, healthcare, and retail. As technology improves, these immersive experiences will become more accessible and widespread. The development of 5G technology will further enhance AR and VR by providing faster and more reliable connectivity. The market for AR and VR is expected to grow significantly, creating new opportunities and transforming various industries.

6. Autonomous Vehicles
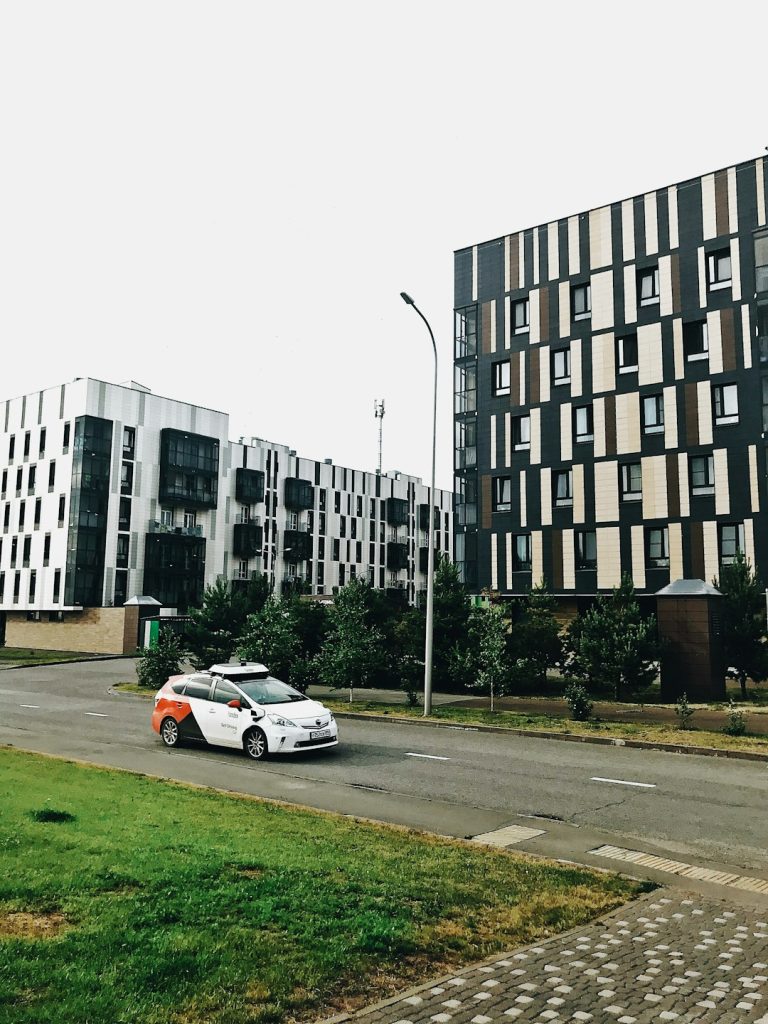

Autonomous vehicles, or self-driving cars, are poised to revolutionize transportation. These vehicles use advanced sensors, AI, and machine learning to navigate without human intervention.
Technological Foundations
Autonomous vehicles rely on a combination of sensors, cameras, radar, and lidar to perceive their environment. AI algorithms process the sensor data to identify objects, predict their movements, and make driving decisions. Machine learning enables the system to improve over time, learning from real-world driving experiences.
Real-World Implementations
Autonomous vehicles are being tested and implemented in various real-world scenarios, such as ride-hailing services, delivery robots, and public transportation. Companies like Waymo, Tesla, and Uber are leading the charge in developing and deploying autonomous vehicles. Waymo’s self-driving cars are being tested on public roads, while Tesla’s Autopilot system provides advanced driver assistance features.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Challenges for autonomous vehicles include regulatory approval, safety concerns, and technological hurdles. Ensuring the safety and reliability of autonomous systems is critical for their acceptance and deployment. Regulatory frameworks need to be developed to address liability, insurance, and traffic laws. Despite these challenges, the future outlook for autonomous vehicles is optimistic, with significant investments driving progress.

Global Impact
Autonomous vehicles have the potential to reduce traffic accidents, improve fuel efficiency, and transform urban planning. By eliminating human error, autonomous vehicles can significantly reduce the number of accidents and fatalities on the road. Improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions contribute to environmental sustainability. Autonomous vehicles also enable new urban mobility solutions, such as shared autonomous fleets and smart transportation systems.

7. Biotechnology

Biotechnology leverages biological processes for industrial and medical applications. Recent advancements include gene editing technologies like CRISPR, which allow for precise modifications to DNA.
Technological Advancements
Biotechnology encompasses a wide range of technologies, including genetic engineering, synthetic biology, and bioprocessing. Gene editing technologies like CRISPR-Cas9 enable precise modifications to DNA, allowing for the correction of genetic defects and the development of genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Synthetic biology combines biology and engineering to design and construct new
